In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, precision and efficiency are critical factors that determine the success of any business. One key component in achieving these goals, especially in cutting and shaping materials, is the band saw blade. As industries continue to demand faster, more accurate cutting methods, the band saw blade has become indispensable in a variety of sectors, ranging from metalworking to woodworking, plastics, and even food processing.
What is a Band Saw Blade?
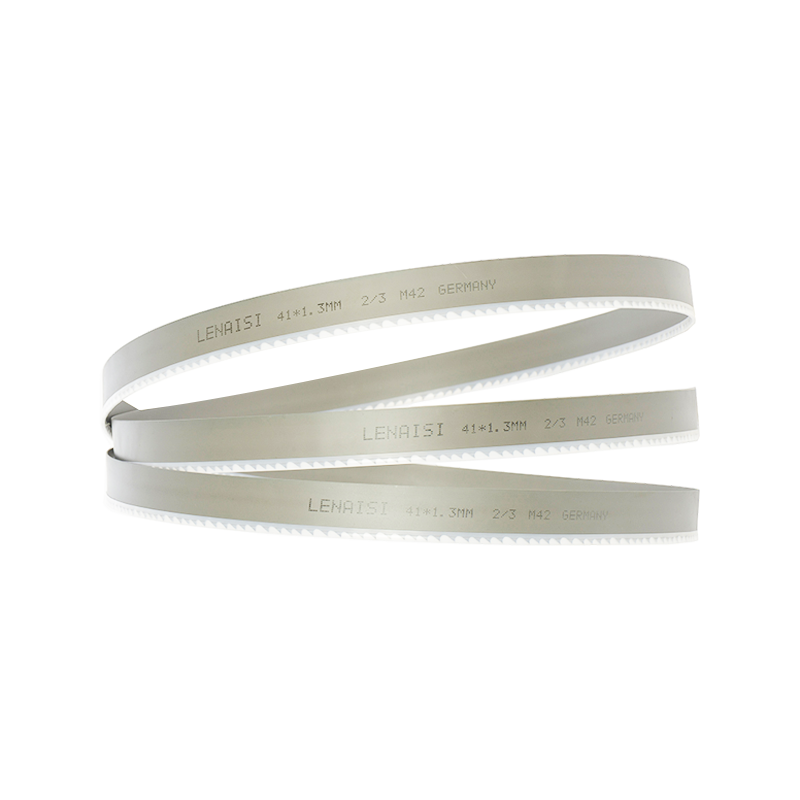
A band saw blade is a long, continuous loop of toothed steel that is used to cut through materials with a band saw machine. It typically runs over two or more wheels, with one wheel being powered by a motor to drive the blade, while the other is used for tensioning. The band saw blade can vary in size, tooth type, and material, depending on the specific requirements of the cutting job. These blades can be designed for cutting wood, metal, plastic, or even delicate materials like food and textiles, making them one of the versatile cutting tools available in industrial settings.
The versatility and precision of the band saw blade have made it a popular choice across various industries, from automotive manufacturing to construction, and even in the production of consumer goods.
Why Band Saw Blades Are Crucial in Manufacturing
1. Precision Cutting
The ability to make precise, smooth cuts is one of the primary reasons the band saw blade is so widely used in manufacturing. Unlike traditional cutting methods, such as hacksaws or circular saws, which often leave rough edges or require additional finishing, the band saw blade delivers clean and accurate cuts. This feature is essential in industries that require high precision, such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics manufacturing.
Furthermore, the band saw blade offers the ability to make intricate cuts, such as curved or irregular shapes, with minimal effort. This flexibility is a significant advantage in industries like custom fabrication, furniture making, and even sculpting.

2. Versatility Across Materials
The band saw blade is incredibly versatile when it comes to the materials it can cut. Different types of blades are designed for cutting specific materials, such as steel, aluminum, wood, plastics, and even food items. By choosing the correct blade for the material being cut, manufacturers can optimize the cutting process, ensuring that each job is completed efficiently and accurately.
For example, blades with high tooth density and bi-metallic construction are often used for cutting hard metals, while blades with wider teeth are used for softer materials like wood. This versatility means that industries of all kinds can benefit from using a band saw blade, as it can adapt to various cutting needs.
3. Increased Efficiency and Speed
Manufacturers today are always looking for ways to reduce production time and increase efficiency. The band saw blade plays a critical role in achieving these goals. With its ability to cut through materials quickly and accurately, the band saw blade minimizes the need for rework or secondary operations. This is especially valuable in high-volume production settings where time is of the essence.
Additionally, modern band saw machines are equipped with features that increase cutting speed, such as automatic feed mechanisms, variable speed controls, and advanced tensioning systems. This allows operators to complete cuts faster and with greater consistency, which improves overall productivity and reduces downtime.
4. Minimal Material Waste
Another significant advantage of using a band saw blade is its ability to reduce material waste. The thin, continuous cutting edge of the blade creates minimal kerf (the amount of material removed during the cut), meaning that more of the material remains intact and can be used for other purposes. In industries where material costs are high, such as metalworking and plastics fabrication, this reduction in waste can translate into significant cost savings.
Moreover, the clean cuts made by the band saw blade eliminate the need for additional finishing steps, further minimizing waste and improving the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.



 english
english Русский
Русский Español
Español Русский
Русский






 CONTACT US
CONTACT US