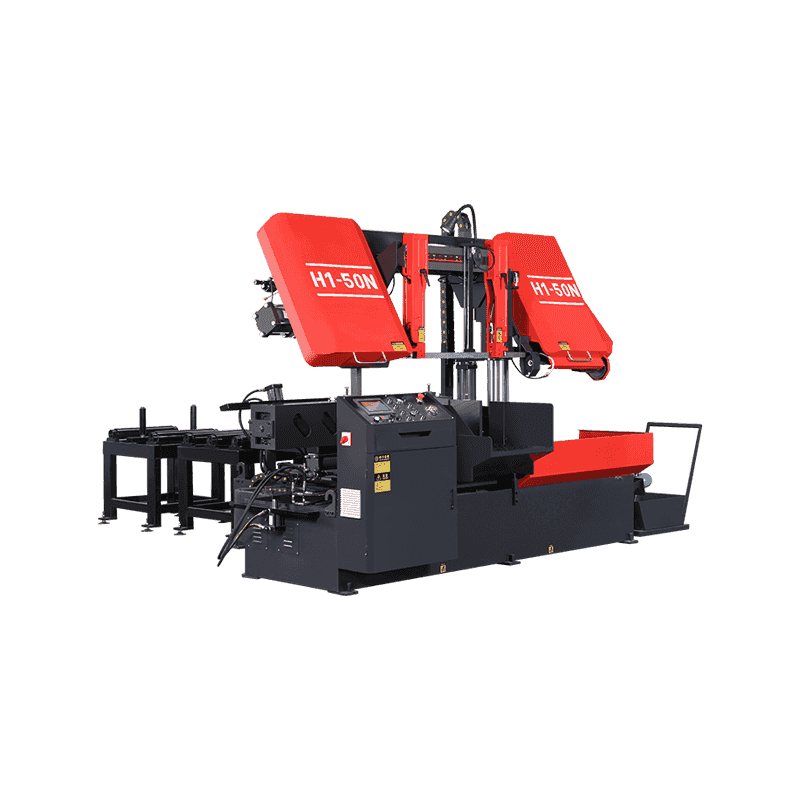
Why Do Workshops Choose Vertical Metal Band Sawing Machine Today?
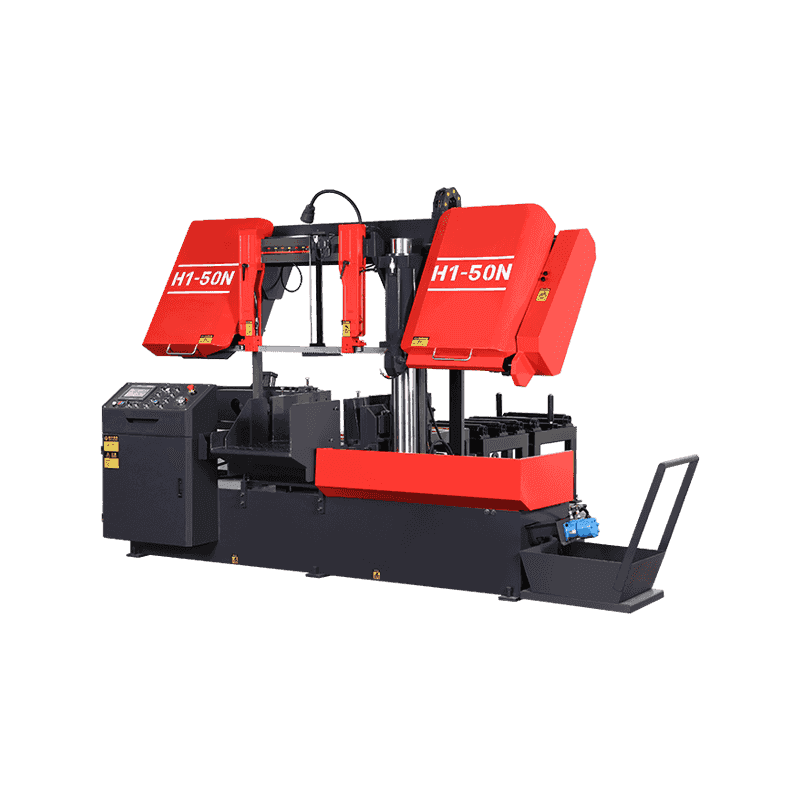
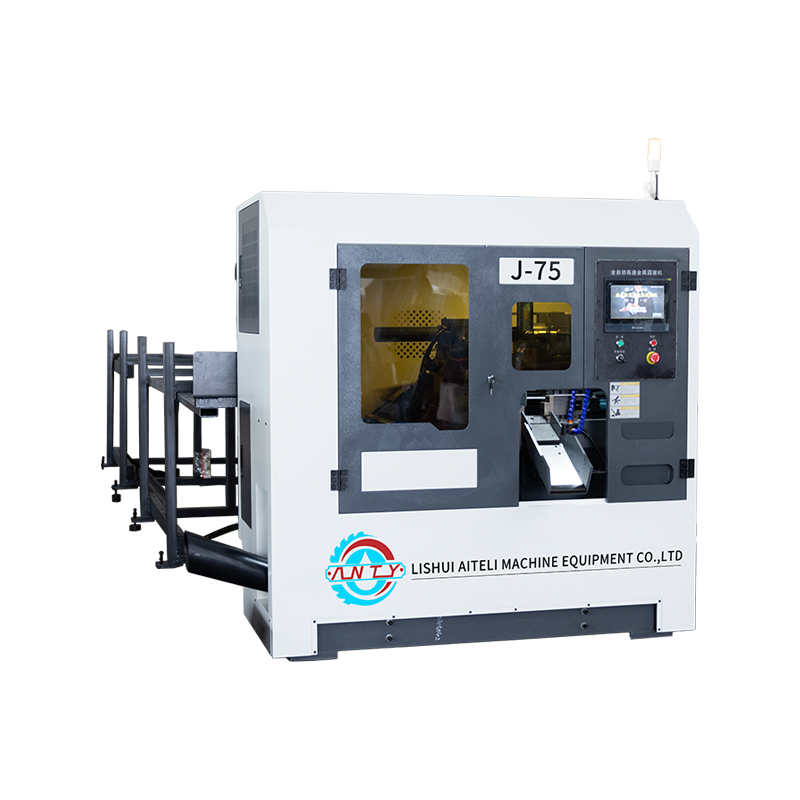
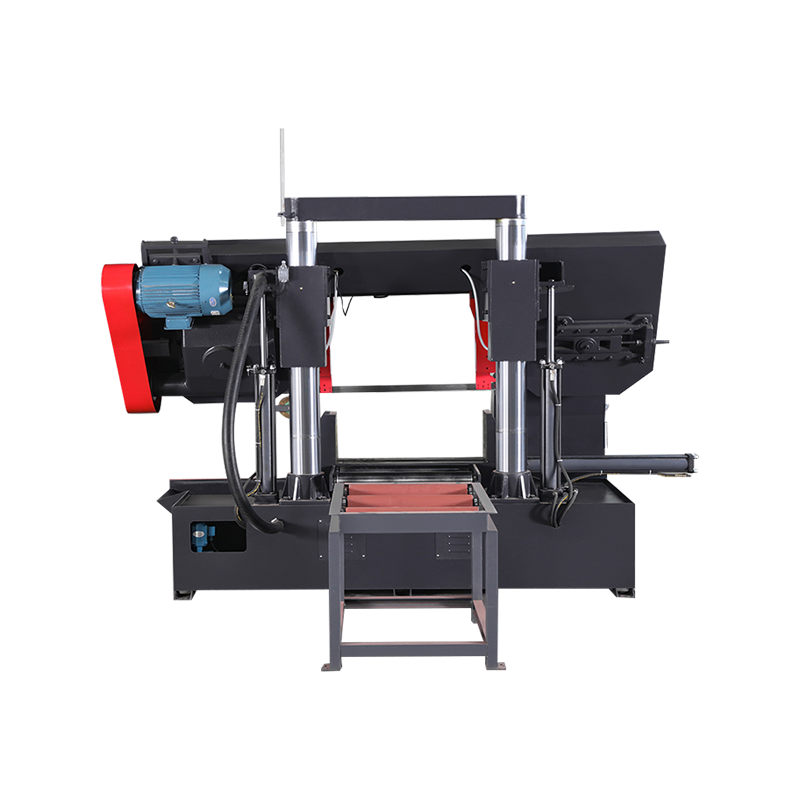
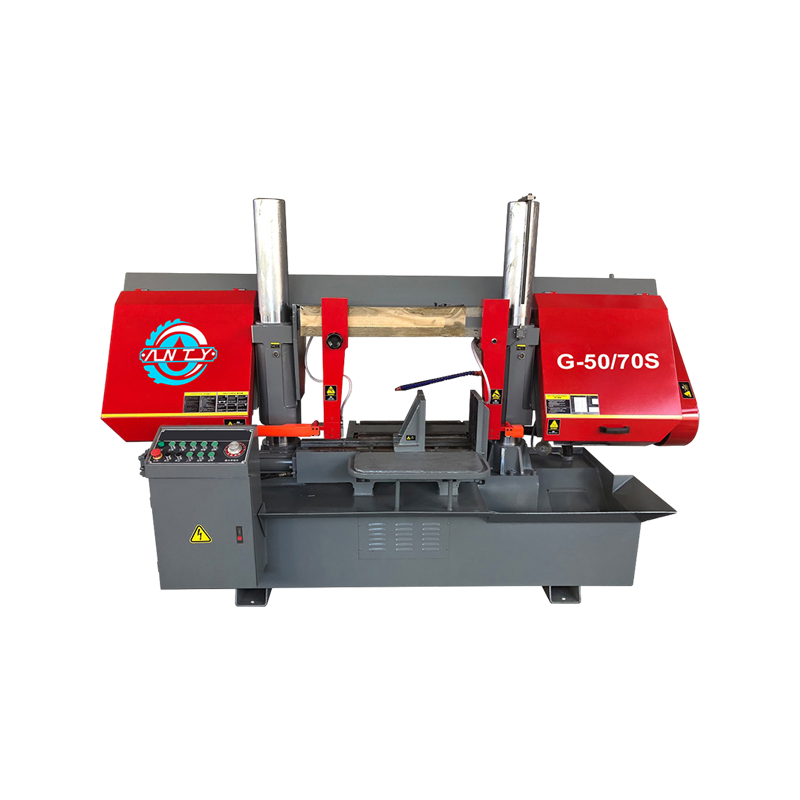
Walk into a modern metalworking workshop and you will notice a clear shift in cutting equipment preferences. Instead of relying on a single type of saw for every task, many workshops now combine different machines to handle diverse materials, tolerances, and production volumes. At the center of this change are two widely discussed solutions: the Vertical metal band sawing machine and the CNC full automatic High speed circular sawing machine. Their growing presence is not driven by trends, but by practical considerations such as accuracy requirements, workflow efficiency, material utilization, and long-term operating stability. Understanding why workshops increasingly select vertical metal band sawing machines today requires looking beyond basic specifications. It involves examining real production challenges, comparing cutting principles, and understanding how these machines integrate into daily operations alongside CNC circular sawing systems. How Vertical Metal Band Sawing Machines Fit Modern Workshop Needs Vertical metal band sawing machines operate with a continuously moving band blade positioned vertically, allowing the operator to guide the workpiece through the cutting path. This structure offers a high degree of flexibility in shape cutting, contour work, and irregular profiles. For workshops handling varied orders, small batches, or customized components, this flexibility plays an important role. Unlike straight-line cutting machines, vertical band saws allow operators to adjust cutting direction during operation. This makes them suitable for tasks such as trimming forged parts, cutting curved outlines, preparing blanks for machining, or separating complex profiles from plates and blocks. Workshops that frequently switch between product types often find this adaptability helpful in reducing setup time between jobs. Another practical reason for their adoption lies in material control. Vertical band saws allow operators to clearly see the cutting area, which improves alignment and reduces unnecessary material removal. This visibility helps lower scrap rates, especially when working with higher-cost alloys or non-standard stock sizes. Precision Control and Cutting Stability in Daily Production Accuracy in metal cutting is not limited to final dimensions; it also affects downstream processes such as milling, drilling, and assembly. Vertical metal band sawing machines are valued for their consistent cutting behavior, particularly when dealing with thicker materials or mixed cross-sections. The continuous band blade distributes cutting force more evenly compared to intermittent cutting tools. This results in smoother cuts and reduced stress on both the blade and the workpiece. For workshops that prepare blanks for further CNC machining, this stability helps maintain dimensional consistency and surface quality, reducing the need for additional corrective processing. Blade selection also plays a role. By choosing appropriate tooth pitch and blade material, operators can adapt vertical band saws to different metals, from carbon steel to aluminum alloys and certain stainless grades. This adaptability supports workshops that do not focus on a single material category. Comparing Vertical Band Sawing Machines with CNC Full Automatic High Speed Circular Sawing Machines While vertical band sawing machines are favored for flexibility, CNC full automatic high speed circular sawing machines serve a different but complementary purpose. These machines are designed for straight, repetitive cuts where speed and consistency are priorities. In many workshops, the two machines are not competitors but partners in the production line. CNC full automatic high speed circular sawing machines use rigid circular blades and automated feeding systems. They are well suited for cutting bars, tubes, and profiles to fixed lengths in large quantities. Their automation reduces manual intervention, which helps maintain uniform results over extended production runs. Vertical band saws, by contrast, are often used earlier or later in the process. They may handle rough cutting, profile shaping, or low-volume tasks that do not justify full automation. Workshops choose vertical band sawing machines today because they fill gaps that automated circular saws cannot efficiently address, especially when production schedules change frequently. Energy Use, Noise, and Workshop Environment Considerations Workshops today are paying more attention to operating conditions, including noise levels, energy consumption, and operator comfort. Vertical metal band sawing machines generally operate at lower noise levels compared to high-speed circular saws, due to their continuous cutting motion and lower rotational speeds. This characteristic makes them suitable for facilities where multiple machines run simultaneously or where noise regulations apply. Lower vibration levels also contribute to improved blade life and reduced mechanical wear, which can influence maintenance planning over time.



 english
english Русский
Русский Español
Español Русский
Русский





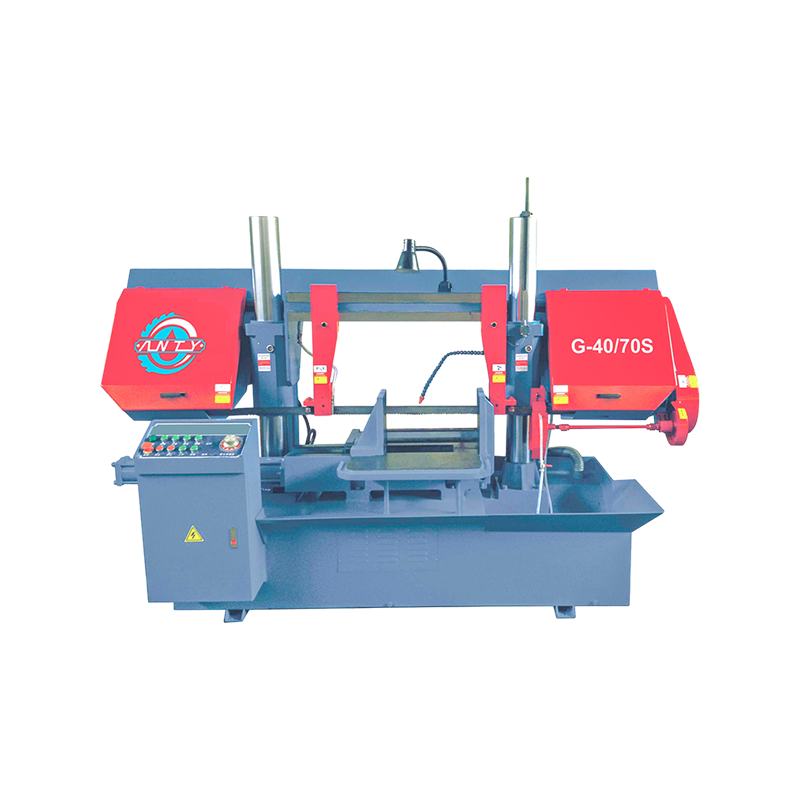





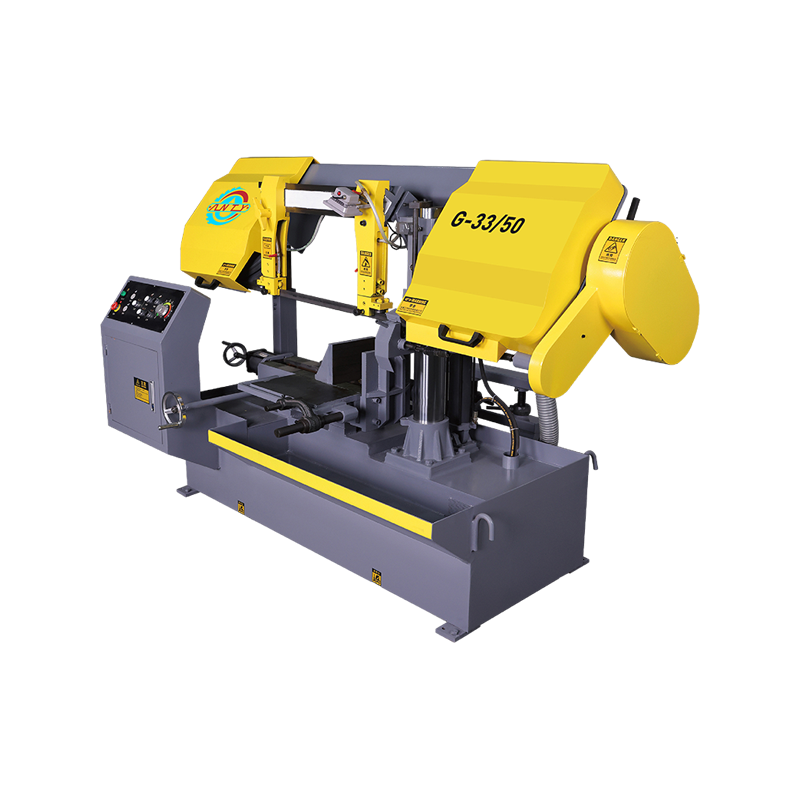
 READ MORE
READ MORE