Operating a Metal Cutting Band Sawing Machine or a Rotary Angle Horizontal Metal Band Sawing Machine requires careful attention to safety and procedural standards. These machines, widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and machinery manufacturing, handle metal materials of varying hardness and dimensions. Ensuring smooth operation is not only a matter of productivity but also of workplace safety. Understanding the proper precautions, handling techniques, and maintenance practices can prevent accidents, improve machine lifespan, and support consistent cutting quality.
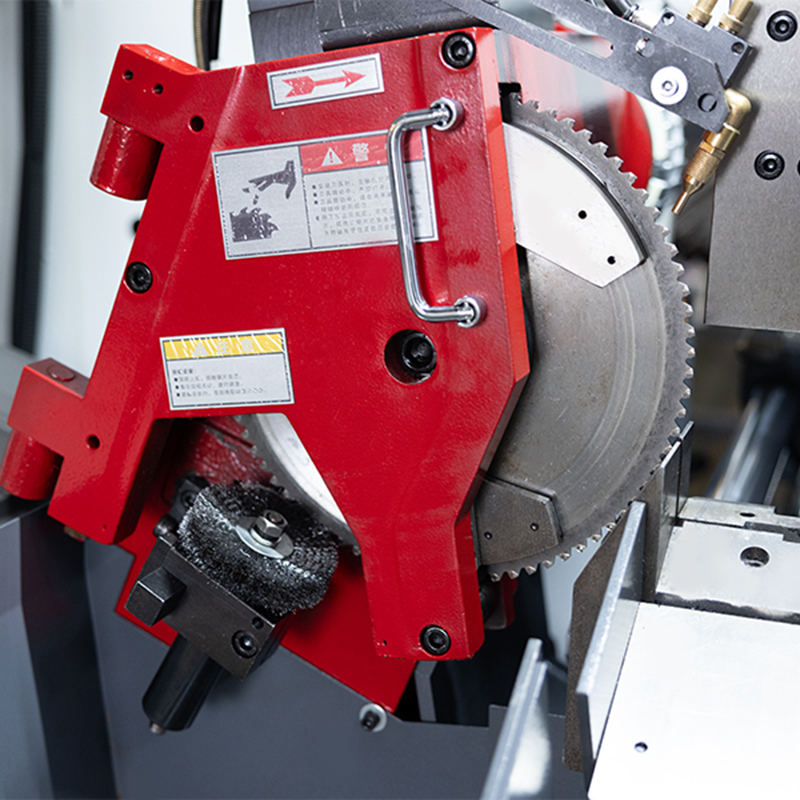
Understanding Machine Setup and Operation
Before starting the machine, it is important to familiarize oneself with its structure and controls. A rotary angle horizontal metal band sawing machine typically allows angle adjustments and automatic feeding functions. Operators should verify that the saw wheel type and cutting range are appropriate for the material and part size. Proper setup includes securing the workpiece firmly, aligning the saw wheel at the desired angle, and checking that all guards and safety covers are in place. Misalignment or inadequate clamping can cause vibration, uneven cuts, or damage to the saw blade.
New users or those transitioning between manual and automatic sawing machines should review operational manuals carefully. Understanding the sequence for starting, feeding, cutting, and stopping the machine helps prevent improper operation. Training sessions can also cover emergency stop procedures, allowing operators to react promptly if unexpected situations arise.
Maintaining Saw Blade and Components
Saw blades on metal cutting band sawing machines undergo significant stress during operation. Regular inspection is necessary to check for wear, cracks, or teeth damage. Using a worn blade can cause inaccurate cuts, increased friction, or potential breakage. In addition to the blade, mechanical components such as the saw wheel, guides, and bearings should be checked for proper lubrication and alignment. Proper maintenance ensures that the rotary mechanism runs smoothly and reduces unnecessary strain on the machine.
Cleaning the machine after each use is also important. Metal debris, dust, and coolant residues can accumulate, affecting the cutting surface and moving parts. Removing these materials prevents unexpected resistance during cutting and lowers the risk of overheating.
Safe Handling During Cutting Operations
While the machine is operating, operators should maintain a safe distance and avoid reaching near moving components. Protective barriers, gloves, and safety goggles are recommended to reduce the risk of injury from flying debris or accidental contact with the saw. For automatic rotary angle sawing machines, monitoring the feeding and receiving functions is crucial. Even if the machine operates automatically, supervision ensures that the workpiece moves smoothly and that jams or misfeeds are addressed promptly.
It is also helpful to use consistent cutting speed and feed rate appropriate for the material. Adjusting the speed too quickly or forcing the feed can stress the blade, increase vibration, and create uneven cuts. Observing the machine during the cutting process allows operators to notice any unusual sounds or motions that may indicate mechanical issues.
Electrical Safety and Workspace Organization
Rotary angle horizontal metal band sawing machines rely on electrical components for motor operation, automatic feeding, and angle adjustment. Ensuring that power cables are in good condition and that the machine is properly grounded reduces the risk of electrical accidents. Disconnecting power during maintenance or blade replacement is essential to avoid accidental startup.
Organizing the workspace around the sawing machine supports both safety and efficiency. Keeping tools, materials, and debris away from moving parts prevents accidental trips or interference with the machine. Adequate lighting and clear floor space also help operators maintain focus and precision during cutting tasks.
Regular Monitoring and Record Keeping
Keeping records of machine usage, maintenance, and inspections provides a practical reference for identifying recurring issues. Scheduled checks on blade condition, alignment, lubrication, and safety features allow operators to address minor problems before they affect operation. Tracking operating hours and performance can also guide decisions about component replacement or adjustments, supporting continuous, smooth operation.



 english
english Русский
Русский Español
Español Русский
Русский






 CONTACT US
CONTACT US